Respect for your privacy is our priority
The cookie is a small information file stored in your browser each time you visit our web page.Cookies are useful because they record the history of your activity on our web page. Thus, when you return to the page, it identifies you and configures its content based on your browsing habits, your identity and your preferences.
You may accept cookies or refuse, block or delete cookies, at your convenience. To do this, you can choose from one of the options available on this window or even and if necessary, by configuring your browser.
If you refuse cookies, we can not guarantee the proper functioning of the various features of our web page.
For more information, please read the COOKIES INFORMATION section on our web page.


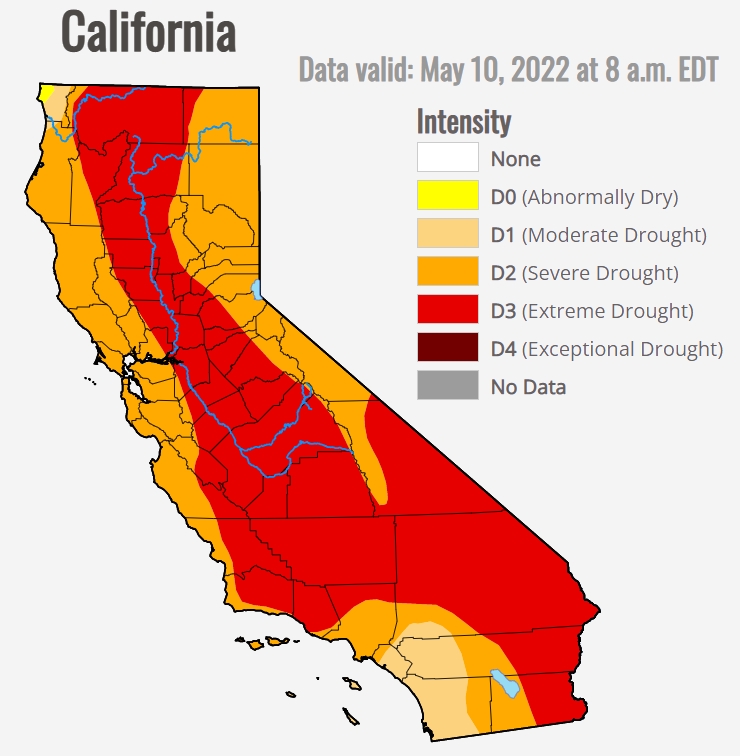 Cameron: “The state is dry from the north end all the way to the south. We’ve had record-low rainfall, and reservoir levels are unbelievably low to where the state [water] allocation for farmers is 5% of normal and the federal water allocation is actually zero. So there are a lot of empty fields that aren’t being planted — something I’ve never seen before. We’re seeing a lot of the almonds that have been planted over the years being taken out just because of the lack of water. I know in Northern California, there’s normally a 500,000 acres of rice, and we know that 270,000 to 300,000 acres will not be produced this year. So what we’re seeing is issues with, I think, food security and a lack of the things that you’re used to seeing on the grocery shelves in the future — they may be a little tougher to find”.
Cameron: “The state is dry from the north end all the way to the south. We’ve had record-low rainfall, and reservoir levels are unbelievably low to where the state [water] allocation for farmers is 5% of normal and the federal water allocation is actually zero. So there are a lot of empty fields that aren’t being planted — something I’ve never seen before. We’re seeing a lot of the almonds that have been planted over the years being taken out just because of the lack of water. I know in Northern California, there’s normally a 500,000 acres of rice, and we know that 270,000 to 300,000 acres will not be produced this year. So what we’re seeing is issues with, I think, food security and a lack of the things that you’re used to seeing on the grocery shelves in the future — they may be a little tougher to find”.


























