Tweaking carotenoid genes helps tomatoes bring their A-game
Researchers led by the University of Tsukuba demonstrated that Target-AID gene editing technology can be used to simultaneously introduce single-base changes into multiple genes in tomatoes. Using this technique, the researchers altered three genes associated with carotenoid accumulation, resulting in elevated levels of carotenoids, particularly lycopene, in the resulting tomato lines. This technology will allow tomato breeders to introduce multiple advantageous gene changes into elite commercial cultivars, bypassing lengthy back-crossing steps between generations.
The popularity of tomatoes has led to the development of more than 10,000 cultivars of various sizes, shapes, and hues. Interestingly though, there is little genetic diversity among modern tomato varieties. This lack of diversity, coupled with the fact that many traits are controlled by multiple genes, makes improving plant yield and quality a major challenge for tomato breeders.
But in a study published this week in Scientific Reports, researchers led by the University of Tsukuba explain how modern gene editing technology may be able to give tomato breeders a helping hand.
"The tomato was the first genetically modified food to be approved for human consumption," says senior author of the study Professor Hiroshi Ezura. "However, many early transgenic varieties contained genes derived from other species, raising safety concerns among consumers. Therefore, coupled with the fact that most transgenic varieties showed only moderate improvements in quality, tomato breeding has, for the most part, moved away from transgenics."
Unlike traditional genetic modification, modern gene editing techniques leave no trace in the genome and can introduce small changes within a native gene, mimicking natural variation.
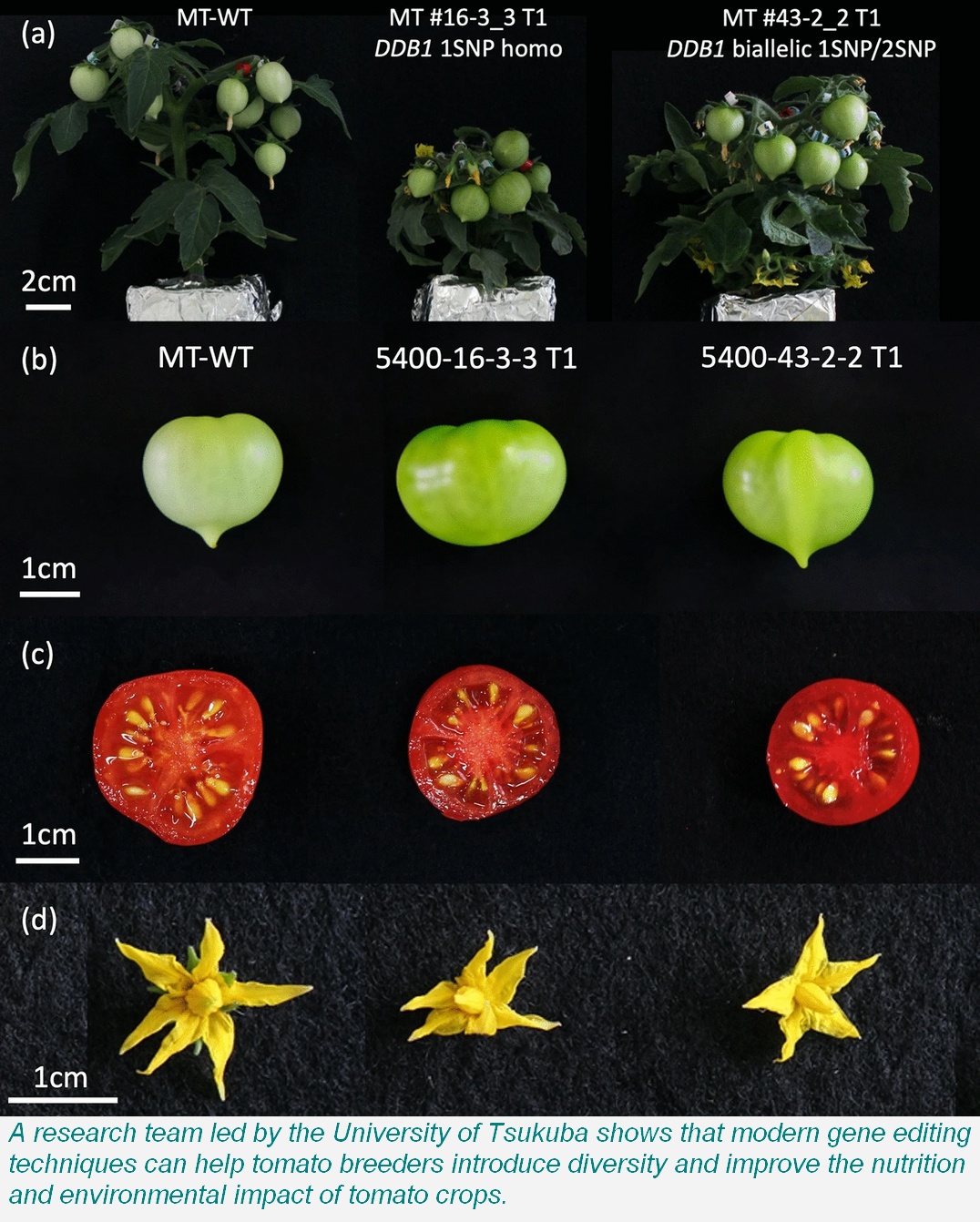

Tomatoes contain relatively high levels of carotenoids, the yellow, red, and orange pigments found in many plants. Carotenoids are precursors to vitamin A and demonstrate antioxidant and anti-cancer properties, making them hugely important to human nutrition. Several natural mutations that enhance carotenoid accumulation in tomatoes have been documented, but their introduction into commercial varieties is a complicated and time-consuming prospect.
The University of Tsukuba-led team therefore set about reproducing carotenoid accumulation mutations in tomatoes using gene editing technology.
"Single nucleotide changes in individual tomato genes had previously been achieved using Target-AID gene editing technology," explains Professor Ezura. "However, we designed a system whereby changes were simultaneously introduced into three genes associated with carotenoid accumulation."
Among 12 resulting tomato lines, 10 contained mutations in all three target genes. Further examination of two lines with the dark green fruit and purple roots of natural carotenoid accumulation mutants revealed high levels of carotenoids, particularly lycopene, in the gene-edited plants.
 Professor Ezura explains, "This shows that it is possible to improve multigenic plant quality traits using gene editing technology, and opens up a whole range of options for improving the yield, shelf-life, nutrient content, and disease resistance of different crop plants, which has obvious benefits for both human health and the environment."
Professor Ezura explains, "This shows that it is possible to improve multigenic plant quality traits using gene editing technology, and opens up a whole range of options for improving the yield, shelf-life, nutrient content, and disease resistance of different crop plants, which has obvious benefits for both human health and the environment."
Some complementary data
The complete study” Multiple gene substitution by Target-AID base-editing technology in tomato” can be found at:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-020-77379-2
Source: phys.org, sciencedaily.com



 Professor Ezura explains, "This shows that it is possible to improve multigenic plant quality traits using gene editing technology, and opens up a whole range of options for improving the yield, shelf-life, nutrient content, and disease resistance of different crop plants, which has obvious benefits for both human health and the environment."
Professor Ezura explains, "This shows that it is possible to improve multigenic plant quality traits using gene editing technology, and opens up a whole range of options for improving the yield, shelf-life, nutrient content, and disease resistance of different crop plants, which has obvious benefits for both human health and the environment."


























