Respect for your privacy is our priority
The cookie is a small information file stored in your browser each time you visit our web page.Cookies are useful because they record the history of your activity on our web page. Thus, when you return to the page, it identifies you and configures its content based on your browsing habits, your identity and your preferences.
You may accept cookies or refuse, block or delete cookies, at your convenience. To do this, you can choose from one of the options available on this window or even and if necessary, by configuring your browser.
If you refuse cookies, we can not guarantee the proper functioning of the various features of our web page.
For more information, please read the COOKIES INFORMATION section on our web page.


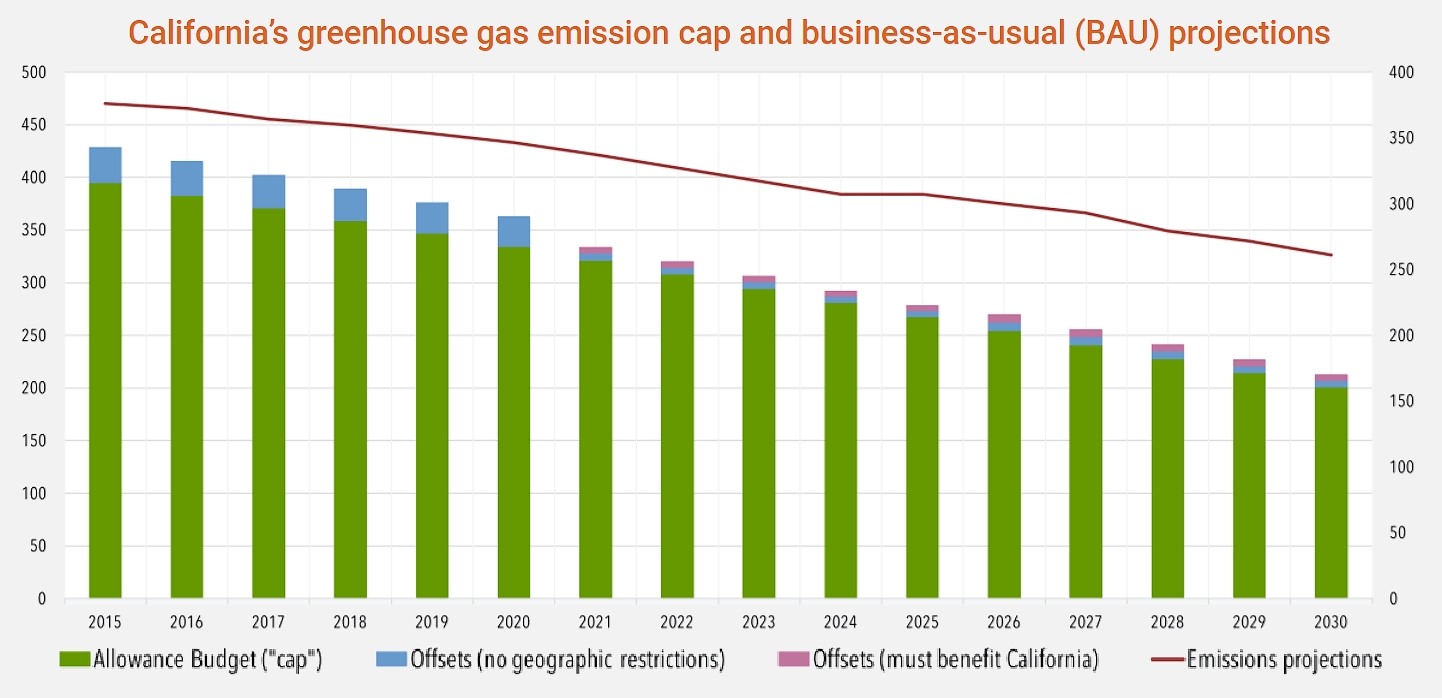
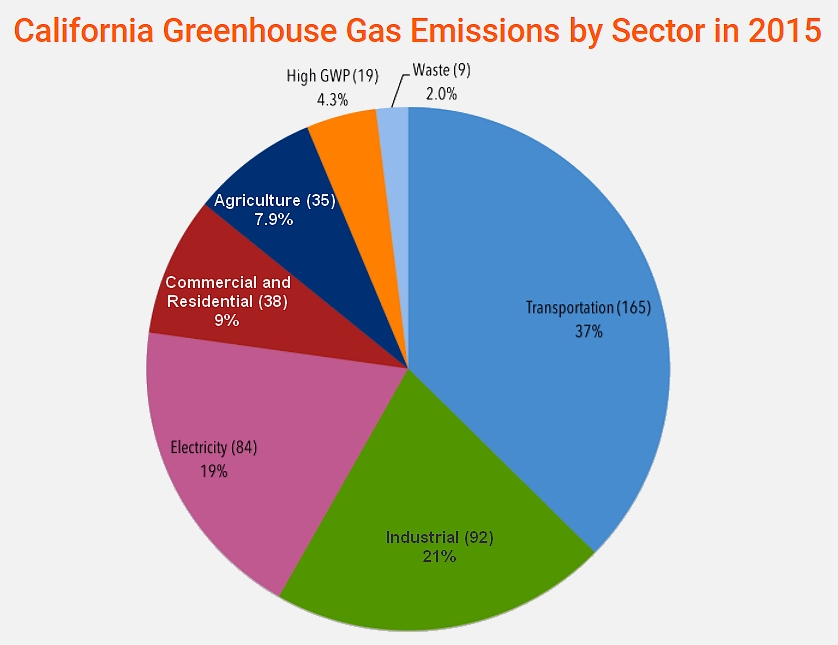 The cap-and-trade rule applies to large electric power plants, large industrial plants, and fuel distributors. Around 450 businesses responsible for about 85% of California’s total greenhouse gas emissions must comply. California has linked its program with similar programs in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec, meaning that businesses in one jurisdiction can use emission allowances (or offsets) issued by one of the others for compliance.
The cap-and-trade rule applies to large electric power plants, large industrial plants, and fuel distributors. Around 450 businesses responsible for about 85% of California’s total greenhouse gas emissions must comply. California has linked its program with similar programs in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec, meaning that businesses in one jurisdiction can use emission allowances (or offsets) issued by one of the others for compliance.